Bartholin’s Cyst : Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Bartholin’s Cyst
Dr. Renu Chaudhary, MS (Ay. Surgery)
Consultant General Surgeon, Shri Dhanwantari Clinic, Ghaziabad
What is Bartholin’s Cyst or Abscess?
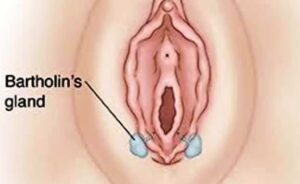
The Bartholin’s glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. These glands secrete fluid that helps lubricate the vagina.
Sometimes the openings of these glands become obstructed, causing fluid to back up into the gland. The result is relatively painless swelling called a Bartholin’s cyst. If the fluid within the cyst becomes infected, there may develop a collection of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue (abscess).
A Bartholin’s cyst or abscess is common. Treatment of a Bartholin’s cyst depends on the size of the cyst, how painful the cyst is and whether the cyst is infected.
Symptoms of Bartholin’s Cyst
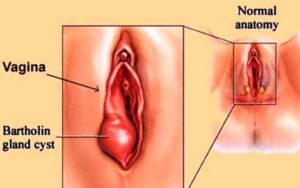 If the size of cyst is small, non-infected Bartholin’s cyst, it may get unnoticed. If the cyst grows, you might feel a lump or mass near your vaginal opening. Although a cyst is usually painless, it can be tender.
If the size of cyst is small, non-infected Bartholin’s cyst, it may get unnoticed. If the cyst grows, you might feel a lump or mass near your vaginal opening. Although a cyst is usually painless, it can be tender.
A full-blown infection of a Bartholin’s cyst can occur in a matter of days. If the cyst becomes infected, you may experience:
- A tender, painful lump near the vaginal opening
- Discomfort while walking or sitting
- Pain during intercourse
- Fever
A Bartholin’s cyst or abscess typically occurs on only one side of the vaginal opening.
Causes of Bartholin’s Cyst
Experts believe that the cause of a Bartholin’s cyst is a backup of fluid. Fluid may accumulate when the opening of the gland (duct) becomes obstructed, perhaps caused by infection or injury.
A Bartholin’s cyst can become infected, forming an abscess. A number of bacteria may cause the infection, including Escherichia coli (E. coli) and bacteria that cause sexually transmitted infections such as Gonorrhea and Chlamydia.
Treatment of Bartholin’s Cyst
Often a Bartholin’s cyst requires no treatment — especially if the cyst causes no signs or symptoms. When needed, treatment depends on the size of the cyst, your discomfort level and whether it’s infected, which can result in an abscess.
Sometimes home treatment is all you need. In other cases, surgical drainage of the Bartholin’s cyst is necessary. If an infection occurs, antibiotics may be helpful to treat the infected Bartholin’s cyst.
Treatment options your doctor may recommend include:
Sitz baths – Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) several times a day for three or four days may help a small, infected cyst to rupture and drain on its own.
Surgical drainage – You may need surgery to drain a cyst that’s infected or very large. Drainage of a cyst can be done using local anesthesia or sedation.
For the procedure, your doctor makes a small incision in the cyst, allows it to drain, and then do the dressing. Daily cleaning and dressing is required for a good healing.
Antibiotics – Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic if your cyst is infected or if testing reveals that you have a sexually transmitted infection. But if the abscess is drained properly, you may not need antibiotics.
Marsupialization – If cysts recur or bother you, a marsupialization procedure may help. Your doctor places stitches on each side of a drainage incision to create a permanent opening less than 1/4-inch (about 6-millimeter) long. An inserted catheter may be placed to promote drainage for a few days after the procedure and help prevent recurrence.
Rarely, for persistent cysts that aren’t effectively treated by the above procedures, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the Bartholin’s gland. Surgical removal is usually done in a hospital under general anesthesia. Surgical removal of the gland carries a greater risk of bleeding or complications after the procedure.
When to see a doctor?
Call your doctor if you have a painful lump near the opening of your vagina that doesn’t improve after two or three days of self-care — for instance, soaking the area in warm water (sitz bath). If the pain is severe, make an appointment with your doctor right away.
Also call your doctor promptly if you find a new lump near your vaginal opening and you’re older than 40. Although rare, such a lump may be a sign of a more serious problem, such as cancer.
Complications of Bartholin’s Cyst
A Bartholin’s cyst or abscess may recur and again require treatment.
Diagnosis and tests for Bartholin’s Cyst
To diagnose a Bartholin’s cyst, your doctor may:
- Ask questions about your medical history
- Perform a pelvic exam
- Take a sample of secretions from your vagina or cervix to test for a sexually transmitted infection
Recommend a test of the mass (biopsy) to check for cancerous cells if you’re postmenopausal or over 40.
If cancer is a concern, your doctor may refer you to a gynecologist who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system.
Prevention and remedies for Bartholin’s Cyst
There’s no way to prevent a Bartholin’s cyst. However, practicing safe sex — in particular, using a condom — and maintaining good hygiene habits may help to prevent infection of a cyst and the formation of an abscess.
** About the author: Dr. Renu Chaudhary is a leading General Surgeon practicing at Shri Dhanwantari Clinic, Ghaziabad since last 15 years. If you have any health problem related to this article, you may contact at our number +91-9818069989 by calling or by sending a message through WhatsApp or you may post your query in the comment box below. Our doctors’ team will answer your query as soon as possible.